Are Insects Smart? Examining the Intelligence of Our Smallest Neighbors
When we think of intelligence, we often envision large brains paired with complex thoughts, a trait commonly associated with mammals and birds. However, insects, which typically have much smaller brains, challenge this notion by exhibiting remarkable behaviors and problem-solving skills that hint at a surprisingly high level of intelligence. While we won’t be assigning any insect a score on an IQ test, the behaviors of certain species suggest that their cognitive capabilities are more advanced than we give them credit for.
This exploration highlights several of the smartest insects found in the United States, showcasing their unique adaptations and behaviors.
Honey Bees
Communication Mastery
Honey bees (Apis mellifera) are remarkable for their complex social structures, living in colonies that function with a high degree of organization. Within these colonies, communication is key to their survival and productivity. One of the most fascinating methods is the waggle dance, which a worker bee performs after discovering a rich floral source.
The waggle dance conveys three crucial pieces of information: the distance to the flowers, the direction relative to the sun, and the quality of the floral resource. This dance is so precise that it’s akin to sharing coordinates on a map, making it a powerful form of communication within the hive.
Tip: To better understand bee communication, observe the way flowers are arranged in any local garden or park. Some flowers attract bees in clusters, creating hotspots that are easily communicated through the waggle dance.

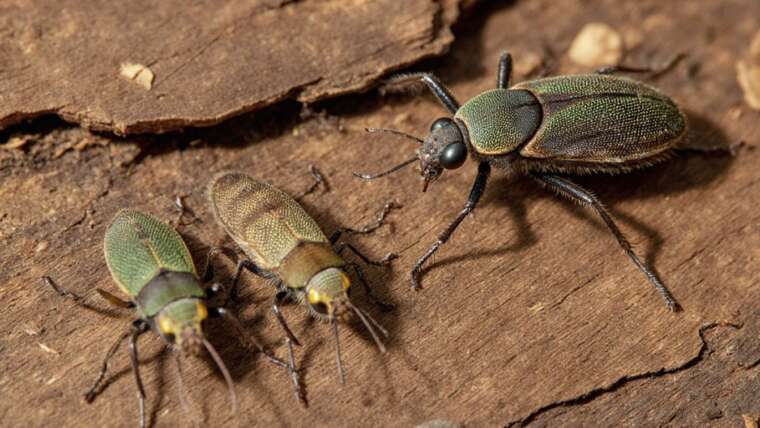
Farmer Ants
Ecosystem Engineers
Many ant species live in highly organized colonies and exhibit intricate forms of communication. A particularly notable group is the farmer ants (such as the Formica and Atta species), known for their unique agricultural practices.
Farmer ants engage in a symbiotic relationship with aphids, tending to them much like cattle, protecting them from predators for nutrient-rich excrement, which they consume. Meanwhile, leaf-cutter ants take this farming to another level by cultivating fungi. They cut leaves and transport them back to their colonies, where the leaves are processed with their saliva to grow fungus, which serves as their primary food source.
Tip: If you see ants carrying leaves or small plant materials, take time to observe their path to the nest, as it can reveal a thriving ecosystem in your backyard while demonstrating the role of ants in local agriculture.
Tarantula Hawk
Survival Strategy
The tarantula hawk wasp is both feared and revered for its potent sting, which can paralyze a tarantula. After incapacitating the spider, the female wasp lays her eggs within the tarantula’s abdomen, ensuring that her larvae have a fresh food supply upon hatching.
What sets these wasps apart is their instinctual intelligence; the larvae expressly avoid vital organs, allowing the tarantula to remain alive for a longer period, maximizing their meal and living space. This method showcases not only survival instincts but also a form of strategic thinking rarely discussed in relation to insects.
Tip: While these wasps might inspire fear, consider directing this interest into researching or visiting local nature centers that may have exhibits on the biology of wasps to better understand their ecological roles and behaviors.
Jumping Spider
Cognitive Abilities
While often categorized incorrectly among insects, jumping spiders (family Salticidae) display commonly recognized signs of intelligence. Many people are familiar with peacock spiders, known for their captivating courtship dances, but these arachnids are also capable of complex problem-solving.
Studies suggest that jumping spiders may possess working memory, enabling them to form strategic plans for hunting and navigating their environments, despite having a brain the size of a sesame seed. This ability to think abstractly and adaptively is astonishing, positioning them as one of the more intriguing species within the arachnid world.
Tip: To appreciate their behavior up close, try setting up a small terrarium with plants and observe how jumping spiders hunt or react to stimuli. This can deepen your understanding of their cognitive skills and enhance your appreciation for these small but mighty creatures.
Understanding insect intelligence not only enriches our knowledge of these fascinating creatures but also aids professionals in fields like pest control, agriculture, and conservation. For further intriguing facts about the world of insects, check out our blog and discover the amazing complexity of these tiny yet impactful life forms.